Telehealth is here to stay. What do you do now?
Technology advancements in the last 20 years have led to a dramatic increase in innovation across the health care spectrum. Revolutionary policymaking has led to an even more staggering adoption of connected healthcare solutions. Telehealth is a primary beneficiary of technology progress through the increased use of connected devices and telecommunication capabilities (e.g., videoconferencing) across the broader population. In 2012, adoption of telehealth was low, with only 36% of states having private payer reimbursement policies for telehealth services. As regulatory restrictions loosened and public/private investments were made, there has been an exponential increase in utilization across the industry.
19x telehealth patient growth from 2013 to 2018; 40 States with telehealth private payer reimbursement in 2019
Due to COVID-19, telehealth is now a necessity, rather than a complementary service, to operate business across the healthcare spectrum. The CARES Act passed by Congress in March 2020 in response to COVID-19 included key provisions to eliminate geographical restrictions for telehealth use in Medicare Advantage plans and ultimately expand access to telehealth and other connected technology services. The FCC allocated $200M in funding to help care organizations provide connected care services. Additionally, in a response to promote telehealth services, many health plans waived cost-share requirements for their members, while expanding paid telehealth services to providers. With these shifts, telehealth companies were catapulted into the healthcare spotlight, and telemedicine has become big business.
US telehealth growth by 2025 projected to exceed $64.1B; Global telehealth growth by 2023 projected to exceed $130.5B
As consumers begin to return to the “new-normal”, many anticipate these regulation exemptions will serve as the foundation to long-standing policies. Driven by the ease of interaction between patient and provider, telehealth adoption will continue to grow and be normalized as another modality of receiving care across the patient care continuum regardless of patient age, disease state, or location. Organizations across all sectors are looking to understand what the future of telehealth should look like for their business, while patients are becoming more aware and accepting of expanded services via telehealth.
60% of patients are willing to see a doctor via remote visit for a chronic condition
90% of physicians now agree virtual care increases access, communication & satisfaction
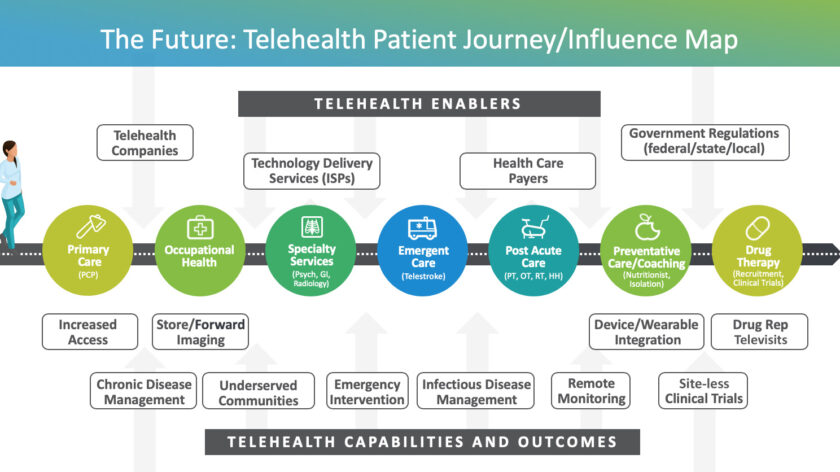
Telehealth patient journey map
Many factors influence the overall utilization and adoption (up or down) of telehealth across a patient’s healthcare journey. A robust and lasting telehealth model should include a more seamless flow of connected stakeholders, including:
- Telehealth Enablers: provide the underlying technologies and policies that enhance and drive the utilization of telehealth
- Care Delivery Players: includes the cross-sector health care stakeholders who deliver care or services through telehealth solutions
- Patients: the end consumers of telehealth services. By enabling telehealth capabilities and services, patients see increased efficiencies and health outcomes.
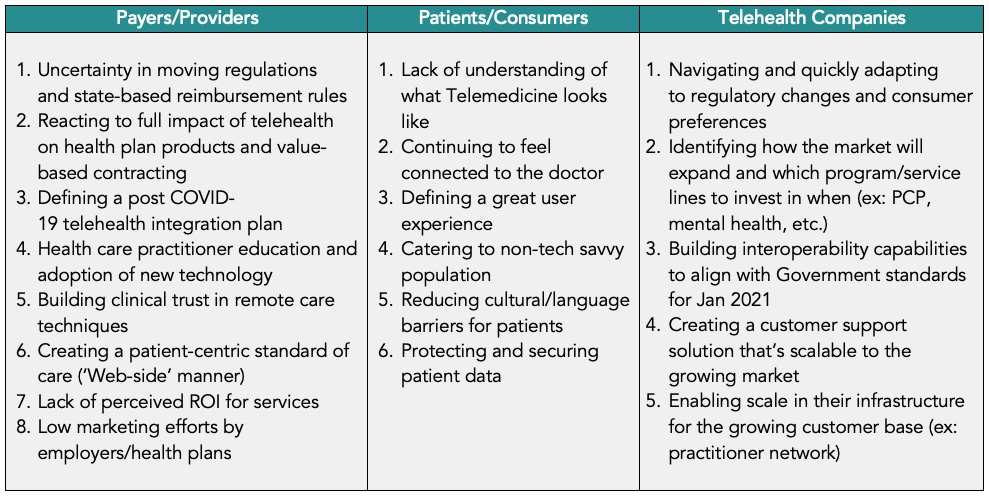
Telehealth challenges
With the growing opportunities and services telehealth can provide, a number of challenges remain and need to be considered carefully when building out a mature capability. While each stakeholder must address their specific hurdles, it is important to also understand broader industry barriers that could impact adoption. The challenges each stakeholder is currently addressing include:
Planning your telehealth journey: unique opportunities in the provider sector
With market conditions driving a shift to a post COVID-19 business model, Providers should utilize a stepwise approach to initiate or accelerate telehealth capabilities. As an organization advances through their telehealth journey, using the following standard approach will help navigate the complex and quickly moving industry.
- Conduct a Maturity Assessment
- Define Organizational Requirements
- Optimize Business and Operating Models
- Prioritize and Build a Roadmap
1. Telehealth maturity assessment
A maturity model enables organizations to baseline competencies and capabilities and provides a framework to assess current state, identify areas of opportunity, prioritize implementation, and benchmark success.
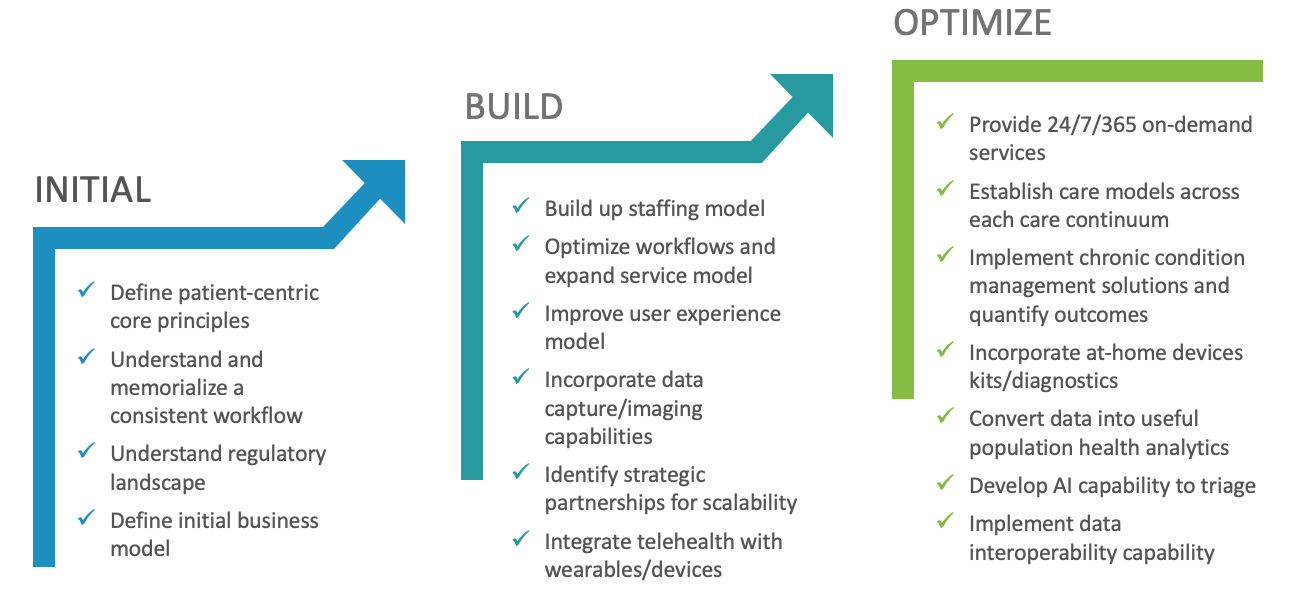
Our maturity model begins with the patient-centric care fundamentals every Provider organization needs in order to support robust telehealth capabilities longer term.
Moving into the next phases of the maturity model allows Providers to focus on scaling the business to multiple business segments and to an expanded practitioner network. Expanded use of technological capabilities (e.g., data/image capture; device/wearable integration) in those future phases allows Providers to focus on improving key patient outcomes.
As part of the maturity assessment, Providers should focus on:
- Measuring your organization against each competency in the Telehealth maturity model
- Documenting telehealth lessons learned across the organization during the COVID-19 timeframe as a pilot
- Understanding current regulatory impacts (current vs. post COVID-19)
- Identifying gaps in current workflows (technology, process, staff)
2. Define organizational requirements
Transitioning from Initial phase to Build phase is a daunting task for any organization. The key to managing this effort is to document business needs and prioritize the timing of each need. Critical considerations at this step include:
- Define short vs. long term service goals
- Segment existing patient population to understand where telehealth capabilities will be most impactful
- Capture cross-stakeholder experience needs to support a telehealth-based workflow and determine minimum workflow requirements
- Identify technology requirements that align with the goals and needs
- App vs. cloud-based solution
- EHR integration
- What services would you want to launch with?
- What scale requirements will you need from the platform provider?
3. Optimizing the business & operating model with telehealth
A key challenge to incorporating a telehealth business model into your organization is understanding long-term viability, including what your ROI will be. Additionally, establishing a complimentary operat
ing model will allow an organization to meet key milestones and quickly adapt to market conditions. Important steps at this phase include:
- Identify target areas across the provider care continuum to rollout telehealth, including areas outside virtual primary care visits
- Model ROI across a realistic timeframe based on various reimbursement expectations and clinical outcomes or value drivers
- Investigate and align incentives for providers to leverage telehealth capabilities
- Define a staffing model that is sustainable and scalable across the maturity journey
- Design a cross-stakeholder, patient-centric telehealth marketing and training program to attract patients and transform how HCPs interact with patients through the new platform and workflows
- Update/adapt existing workflows and compliance expectations to align with clinical guidelines (e.g., provider credentialing; HIPAA compliance standards)
- Identify inter/intra-operability with existing EHR technology
4. Prioritize and build your roadmap
Due to the rapid pace at which telehealth is evolving, a formal roadmap is necessary to keep up with the market. This roadmap will serve as an organization’s playbook to organize and trigger effective actions. Some elements include:
- Governance model that drives smart and speedy decision-making as reimbursement rules and government regulations change frequently
- Organizational goals that include financial budgeting and planning to account for all the cross-functional stakeholders that will be impacted by the telehealth strategy
- Distinct milestones with owners to visually indicate progress so the overall team can see important horizon points of the telehealth journey
- Market assessment to identify potential vendor partnerships to ensure capability gaps are vetted and analyzed
As health plans and regulatory agencies reduce the tension around telehealth capabilities in a post COVID-19 world, providers will be put in a prime position to capitalize on the cost-saving opportunities that a robust telehealth capability can provide, specifically with chronic disease management and remote monitoring. Defining your organization’s core principles and beginning to build the foundational blocks of telehealth now will allow providers to maximize the advancements in technology and expansion of niche models in the telehealth industry.
Contact us to find out how Vynamic can support a current assessment of your Telehealth maturity model and help develop your Telehealth roadmap for the future.
End notes
- Abrams, Ken, et al. “What Can Health Systems Do to Encourage Physicians to Embrace Virtual Care?” Deloitte Insights, July 2018, www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/health-care/virtual-health-care-health-consumer-and-physician-surveys.html#infographic.
- “http://Go.americanwell.com/Rs/335-QLG-882/Images/American_Well_Telehealth_Index_2017_Consumer_Survey.Pdf.” American_Well_Telehealth_Index_2017_Consumer_Survey., American Well, 2017, go.americanwell.com/rs/335-QLG-882/images/American_Well_Telehealth_Index_2017_Consumer_Survey.pdf.
- “State Telehealth Laws & Reimbursement Policies.” Thumbnail, Public Health Institute / Center for Connected Health Policy, 2020, http://www.cchpca.org/telehealth-policy/current-state-laws-and-reimbursement-policies#.
- Statista Research Department. “Forecasted Number of Telehealth Patients Worldwide 2013-2018 .” Statista, Statista Research Department, 17 Jan. 2014, http://www.statista.com/statistics/302641/global-telehealth-market-patients/.
- “Telehealth Basics.” ATA, http://www.americantelemed.org/resource/why-telemedicine/.
- “Telehealth Index: 2019 Physician Survey.” Telehealth Index: 2019 Physician Survey, American Well, 2019, static.americanwell.com/app/uploads/2019/04/American-Well-Telehealth-Index-2019-Physician-Survey.pdf.
- Ugalmugale, Sumant, and Rupali Swain. “Telemedicine Market Share Report: Global 2020-2026 Industry Data – Industry Coverage.” Global Market Insights, Inc., 2020, gminsights.com/segmentation/detail/telemedicine-market.
About Vynamic
Vynamic, an Inizio Advisory company, is a leading management consulting partner to global health organizations across Life Sciences, Health Services, and Health Technology. Founded and headquartered in Philadelphia, Vynamic has offices in Boston, Durham NC, New York, and London. Our purpose is simple: We believe there is a better way. We are passionate about shaping the future of health, and for more than 20 years we’ve helped clients transform by connecting strategy to action.
Through a structured, yet flexible delivery model, our accomplished leaders work as an extension of client teams, enabling growth, performance, and culture. Vynamic has been recognized by organizations like Great Place to Work and Business Culture Awards for being leaders and innovators in consulting, company culture, and health. Visit Vynamic.com to discover how we can help transform your
organization or your career.
Want to learn more? Get in touch!
Other insights.
Jump to a slide with the slide dots.
Scenario Planning Infographic
Boost launch readiness with scenario planning. Learn 5 steps to stay proactive in today’s unpredictable market. Download the infographic.
Read more Brian Stamm
Brian Stamm
AI-Powered Decision Making to Simplify Your Launch Journey: Vynamic Experts on LaunchNav
LaunchNav by Inizio simplifies pharma launches with AI-driven insights, real-time benchmarks, and 800+ launch learnings.
Read moreThe One Big Beautiful Bill Act: Implications for the U.S. Health Industry
OBBBA reshapes U.S. healthcare with $1.2T cuts, shifting risk to providers, payers, and pharma. Explore impacts and strategies.
Read more
